Table of Contents
Color
A number of functions to deal with colour images
Convert Stack to RGB
Converts a 2 or 3-slice stack to an RGB image assuming that the slices are in R, G, B order. The stack must be 8-bit or 16-bit grayscale.
Convert to Composite
Converts an RGB image or stack with 2-7 slices into a composite color stack.
RGB Split
Splits an RGB image into 3 8-bit greyscale images that hold the R, G, B components of the original. The window names have an appended (red), (green) and (blue).
When using hyperstacks, this command splits the data into channels.
RGB Merge
Merges 1, 2, or 3 greyscale images into an RGB image. Select *None* to keep a channel empty (filled with 0). Check Keep source images if you wish to keep the originals.
Show LUT
Displays a plot of the active image's lookup table. The lookup table, or color table, describes the color that is displayed for each of the 256 possible pixel values. For 16 and 32 bit images, the range of displayed pixel values is mapped to 0-255. A bar under the plot displays the color representation of the pixel values. Note that RGB color images do not use a lookup table.
Edit LUT
This option calls the LUT Editor.
Click on a particular LUT entry to edit the Red, Green and Blue entries
[image here]
You can drag a range of entries, the plugin will ask to define the RGB starting and last entries of the selected range and will fill the remaining ones using the method selected in Set… (Replication, Interpolation or Spline Fitting).
You can also define the number of entries in the LUT wih the Number of Colors option. This will fill the LUT with the number of colours, evenly spaced over the LUT space. Replication just repeats the entries while Interpolation and Spline Fitting produce gradations between the colours.
The Invert button sets the inverse of the LUT RGB entries. Open and Save allow importing or exporting the LUTs.
Color Picker...
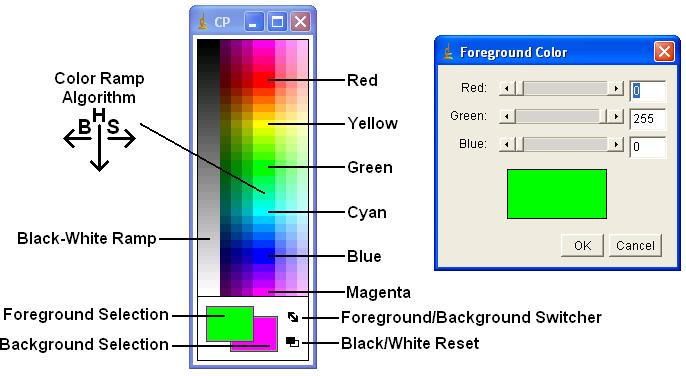
The Color Picker tool enables the user to select foreground and background colors, which affect Edit/Fill, Edit/Draw and other color drawing commands. It displays current foreground and background colors in the selection boxes at the bottom of the window. It has two modes: foreground and background. To change modes, click on the desired selection box. Clicking on the Foreground/Background Switcher button sets the current foreground to the background and vice versa. The Black/White Reset button sets the foreground to black and the background to white.
[Color Picker] The color palette is based on HSB (Hue, Saturation and Brightness) color model. Hue increases as you go down the palette while saturation and brightness values are split horizontally. The left half of the palette varies only in brightness while the right half varies only in saturation. At the center of the color ramp are enlarged red, green, blue, cyan, magenta, and yellow colors for quick selection. To the left of the color palette is a grayscale ramp that goes from pure black to pure white.
Double-clicking on a color brings up the Color Selector, shown on the right in the illustration. Use the sliders to specify the RGB values of the foreground or background color. To get precise colors, manually change the values in the text boxes. The title of the Color Selector window (“Foreground Color” or “Background Color”) indicates the current selection mode.
The Color Picker was written by Gali Baler, a 2003-2004 intern from Bethesda-Chevy Chase High School.