Table of Contents
OpenMIMS
OpenMIMS is an ImageJ plugin designed to open, process and analyze images captured with NanoSIMS 50 & 50L secondary ion mass spectrometers (Cameca).
Introduction
The OpenMIMS plugin has been developed at the National Resource for Imaging Mass Spectrometry (NRIMS, http://www.nrims.hms.harvard.edu), an NIH-supported National Resource developing Multi-isotope Imaging Mass Spectrometry (MIMS) for biomedical research. Images and/or stacks of images of up to 7 different isotopes can be opened, analyzed and saved. Image ratios and Hue-Saturation-Intensity (HSI) maps of any combination of isotopes can be displayed and data from any number of Regions of Interest (ROIs) extracted, analyzed and tabulated for single images or entire stacks.
Features
- Open, process and analyze images captured with NanoSIMS 50 & 50L secondary ion mass spectrometers.
- QSA and dead time correction.
- Generate Hue Saturation Intensity images.
- Generate plots and tables for Regions of Interest (ROIs).
- Generate reports.
- Export images in png format.
Download
- SampleData1 (4 masses, single plane, 1.1Mb)
- SampleData2 (7 masses, 292 planes, 90Mb)
Installation
To install the OpenMIMS plugin, extract the contents of the Open_MIMS.zip file into the “plugins” directory under ImageJ. Only the .jar files need to be the placed in the “plugins” directory. The files README_OpenMIMS.txt and MimsManual.pdf are documentation files and are not required by the OpenMIMS plugin.
Once the contents are copied over, restart ImageJ or use the Update Menu command. “Open MIMS Image” should now appear under Plugins menu. Note this plugin requires a 1.43u or later version of ImageJ (http://rsb.info.nih.gov/ij/download.html) and Java 1.6.
Application Description
MIMS Data
The MIMS Data tab displays a subset of the image's meta-data including the absolute path of the current image, the number of masses and their AMU values, number of planes in the stack, position, date of image, user name, dwell time, duration, raster size and image size. The Synchronize Stacks check box enables updating of all masses simultaneously while scrolling through an image stack. Adjusting the slider (plane selector) at the bottom of any mass automatically selects the same plane for all masses.
Process
The Process tab allows the user to generate ratio images and HSI maps. Ratio and HSI images are the result of dividing one mass image by another. Masses that have similar masses will automatically show up in list form in the Process tab. Others that do not show up by default can be entered manually using the Add… button. A ratio image will appear when the user selects one (or more) in the list and clicks Display Ratio. When moving the mouse pointer over the ratio image, the status box along the lower border of the NRIMS Analysis Module window displays the raw numerator and denominator counts as well as the ratio value.
HSI images are similar to ratio images but are different in that they use a combination of the the ratio value of a pixel, the counts of one of the masses for the intensity, and a constant saturation value, to generate pixels in the RGB color space. Clicking the Display HSI will make the selected HSI image appear. An example HSI image is provided in APPENDIX A of the OpenMIMS manual. When displaying HSI images, the user has the option of displaying the actual ratio values (multiplied by the Ratio Scale Factor) or displaying percent turnover by selecting the Percent Turnover radio button. Percent turnover is determined by the naturally occurring ratio of that specific isotopic pair along with the maximum achievable ratio based on the experimental protocol.
The Threshold option sets the minimum number of counts in the numerator and/or denominator. Any pixels below that threshold will be ignored and appear black. The Ratio Range Min and Max values determine the range of the colormap used to display the image. The RGB Min and RGB Max values determine the intensity scale used in the image. The Transparency selects the method for computing the intensity component of the HSI image, and the Label option enables a color scale bar to be become visible. Selecting the Use Sum radio button will generate a single HSI (or ratio) image representative of the entire stack. Selecting the Use Window radio button will use the sum of both masses over a sliding window with the specified window size. This can be very useful for finding small features in large image stacks that have low counts. Also, a median filter can be applied to a ratio or HSI image by selecting the Median Filter Ratio radio button.
Contrast
The Contrast tab allows the user to control the contrast settings, by adjusting the sliders, for any given mass, ratio or sum image (HSI images do not have contrast settings, instead their display parameters are controlled using the Process tab). It also displays a histogram of intensity values for any of these types of images. Clicking on an image brings it into focus and the histogram and contrast settings will update to reflect the values of the current image in focus. The histogram and contrast settings will also update by selecting the window in the combobox located at the bottom of the Contrast tab. All mass, ratio and sum images should appear in the combobox.
If changes to the default contrast settings are made, clicking the Reset button will bring those settings back to their default values. Clicking Auto will iterate through a set (usually 5 or 6) of contrast settings, eventually returning back to default values. The Set button allows the user to input values for min and max that are outside the range of those provided by the Minimum and Maximum sliders.
Mass, ratio and sum images can also be set to Auto Adjust meaning that each time a new slice is selected in the stack, new contrast settings are calculated. If Auto Adjust is not selected, the contrast settings for the first image in the stack are used throughout the stack.
The user has the additional capability of displaying the image using Lookup Tables other than the gray table used by default. There are several options for displaying the data and each image can be set independently.
Stack Editing
The Stack Editing tab is reserved for functions that relate to the editing and manipulating of mass images. This includes deleting and reinserting planes, applying translation, compressing the image and generating sum images. One important thing to note is that there are two indices for an image, both of which are displayed: True index and Display index. The True index of a plane in an image never changes, but the Display index depends on what planes have been deleted. For example: entering “1-5” and clicking the Delete, then entering “6-10”, and clicking “Delete” will -not- delete the first 10 planes of an image. Doing that is equivalent to entering “1-5, 11-15” and clicking Delete. The Reinsert button uses the indices of the original data, so entering entering “1-5, 11-15” would reinsert the previously deleted planes.
A plane that is currently displayed can be translated using the Translate X or Translate Y spinners, or by entering a value those text fields. The image can also be registered automatically by clicking on a specific mass to use and then clicking the Autotrack button. This will call the autotrack algorithm which will automatically attempt to determine the best per image translations for a best fit alignment throughout the stack. Clicking Untrack will reset all translations to zero.
The Concatenate button allows another image (or image stack) to be prepended or appended to the current image set. The Sum button will generate a sum image from whichever mass image or ratio image was most recently clicked. If the field is blank the entire image is summed, or a range of planes can be entered in the textfield (e.g. 1-20). The Compress button compresses the images into blocks of the size entered in the text field. Entering a value of 4 in the field will sum the pixel values in blocks of 4 planes, resulting in a stack of images 1/4 the original size. Any remaining planes at the end of the stack are summed together into a single block. The Uncompress button undoes the compression and restores the image to its original state - minus any translations applied and planes deleted.
Tomography
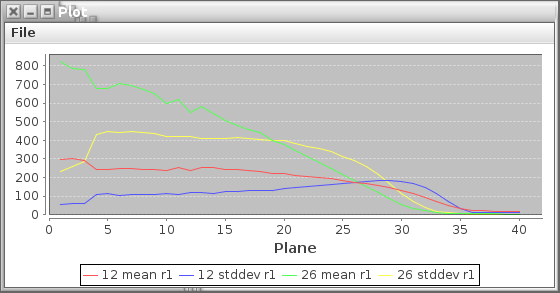
The Tomography tab allows the user to generate simple line plots or tables of ROI statistics through the stack. Simply select a set of ROIs from the ROI Manager, the desired statistics, and the mass, ratio and/or sum images and click Plot or Table. The Planes field allows the user to enter which planes are included in the plot (or table). If this field is left blank, all planes will be included. Checking the Append box will append the data to an existing plot or table if one exists, otherwise a new one will be created. An example of the type of plot produced can be seen below.
The table output will vary depending on the type of images for which statistics are being generating. Mass and ratio images that are more than one plane will output one row of data per plane. In the case of sum images and other images that are only one plane, one row of data will be produced per ROI.
The right side of the tab includes a histogram that displays the intensity values for the pixels within a given ROI. To set which ROI values are displayed by the histogram, the user only needs to scroll the mouse over the desired ROI. After a ROI has been drawn, it can be moved anywhere within the image by either dragging it with the mouse, or using the position spinners in the ROI Manager. If the Autoupdate Histogram radio button is selected, the histogram will update as the ROI is being moved by the mouse. Otherwise, it updates when the move is complete.
A line ROI represents a special case because it has no enclosed area, so its values will not be represented in the histogram. Instead, the user can select the Dynamic Profile button to generate a profile plot of the pixels which the line intersects.
Segmentation
The Segmentation tab allows the user to perform an algorithmic segmentation of a MIMS image to automatically generate ROIs for a given image plane. The algorithm used is a support vector machine (SVM) based segmentation that classifies pixels in the image using methods similar to Fuller et. al}. A full description of SVMs is outside the scope of this document but will be detailed in a forthcoming paper. The algorithm can use many values or features to classify a pixel: the value of that pixel in a set of mass or ratio images, the mean and standard deviation in a neighborhood around that pixel, and the gradient around that pixel. Note that the ability to use other features may be added later. To perform a segmentation the user clicks on the Config button. The Export button will export the SVM and data if the SVM has been trained using the libSVM format.
Here the user may select which mass and ratio images to use for the segmentation (segmentation can not be performed on Sum images). One can choose whether or not to use the Neighborhood parameters (mean and standard deviation) and the Gradient as features, as well as the size of the neighborhood radius. Some parameters used by the SVM library (in our case libSVM [2]) ned to be set by clicking the Setup button, specifically the type of kernel to use and the level of cross validation. We recommend using the radial basis function (RBF) as the kernel. The level of cross validation may be reduced to increase speed at the possible cost of accuracy.
To train the SVM the user needs to choose at least several ROIs that represent a given class of pixels. First a class is added to the Class Manager by clicking the Add button. Then the representative ROIs are drawn. Then the Sync button is clicked to sync the ROIs in the ROI Manger to the class in the Class Manager. Finally the users clicks the Ok button to complete the SVM configuration.
MIMS Log
The MIMS Log tab keeps a record of what the user has done: e.g. deleting planes, translating planes, autotracking, etc. Various bits of degub data are also displayed on this tab. This information is not saved and is most likely of little use to the most users.
ROI Manager
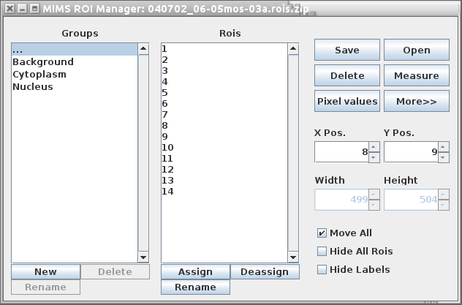
The ROI Manager (see below) gives the user functionality relating the ROIs in a given image. It is comprised of two lists, one labeled Groups and one labeled Rois, as well as a panel on the right hand side containing buttons, spinners and checkboxes.
To create a ROI, first select the type of ROI to draw by clicking one of the corresponding toolbar buttons in ImageJ's main window (any of the five buttons on the left, i.e Rectangle, Circular, Polygon.. etc, see the top right window in Figure 2). Then place the mouse over the area and drag the mouse while holding the left mouse button down. When the left mouse button is released, the corresponding ROI will appear in all image windows as well as in the list of ROIs in the ROI manager. Clicking on a previously drawn ROI in ROI Manager list will automatically highlight the selected ROI in all mass, ratio, sum and HSI images.
The Groups list allows the user to organize ROIs into groups. The user can create new groups, delete existing ones, and assign ROIs into groups. An ROI can only belong to a single group. Clicking on a group will reduce the Rois list to only those ROIs belonging to that group. Clicking on the elipses group(…) will always show all ROIs.
Delete will delete the selected ROIs in the ROI list. If none are selected then it will delete them all, after prompting the user. Rename allows the user to rename the ROI from its default name. Open will open an ROI file that had been saved from a previous session and overwrites the current list. Save will save a single ROI to a file or a group of them to a .zip file. Measure will open a statistics box that will display statistics for all ROIs for the current image. Deselect will deselect any ROIs that have been highlighted. The More» button offers the user some more complicated features relating to the combining and splitting ROIs. ROIs can be moved on a pixel by pixel basis using the X Pos. and Y Pos. spinners. ROIs can also be moved by the user by dragging them across the image with the mouse cursor. Adjusting the Width and Height spinners will adjust those values but only for rectangular and circular ROIs.
If the user moves an ROI, it will move for all images in the stack unless the Move All checkbox is unchecked, in which it will only be moved for the current plane. The user can choose to hide all ROIs by checking the Hide All Rois checkbox or just hide the labels by checking the Hide Labels checkbox.
Menu Items
- File > Open MIMS Image: This menu item will bring up a file chooser that allows the user to select which file should be opened. The plugin can read .IM files and .NRRD files (It can only open the .NRRD files that were generated by the plugin). Additionally it can open any .RATIO, .HSI, .SUM, .ROI and .ROIS.ZIP file that was generated by the plugin when saving from a previous session.
- File > Save Image: This menu item will save whatever modifications have been made to the original .IM file (translations, dropped planes, etc.) into a new binary file with a .NRRD file extension. The OpenMIMS plugin is capable of reading the both .IM files and the .NRRD files that it generates.
- File > Save Session: This menu item is similar to the “Save Image” menu item however in this case additional files will be created for each ratio, hsi and sum image that is open at the time of saving. These files can be opened individually at a later date so long as the .NRRD file that was created with them is stored in the same directory.
- File > About OpenMIMS: Displays version and other information related to the OpenMIMS application.
- Edit > Preferences: Opens a dialog box which allows the user to set customized preferences.
- Edit > Restore MIMS: This menu item will reset the current image to its original state, all translations will be set back to zero and all dropped images will be reinserted. Functionally it is the same as reopening the current image.
- View > Tile Windows: This menu item will take all of the currently open image windows and rearrange them in a grid on the desktop.
- View > ROI Manager: This menu item open the ROI Manager. The ROI manager will also open whenever a ROI is drawn.
- Utilities > ImageNotes: Opens up a text area that allows user to enter notes regarding an image. These notes will be stored with other metadata when saving the file.
- Utilities > Generate Report: Opens a dialog box which captures the current image and has a text area that allows the users to enter notes. When the user clicks OK a .RTF formated report is generated. Subsequent images and notes can be appended to the report. This functionality is useful for recording important information while analyzing images.
- Utilities > Sum All Open: Generates a sum image for all open mass and ratio images. It will not generate a sum image for open HSI images. See the Process section to see how to generate sum images for HSI images.
- Utilities > Import .im List: The OpenMIMS application has the ability to read a text file with a list of file names and it will open those image files, appending them to one another. (NOTE: All image files must exist in the same directory as the text file that references them.) An example image list file is provided in APPENDIX D of the OpenMIMS manual.
- Utilities > Capture Current Image: Selecting this menu item will produce a screen capture of the last image clicked by the user (whichever image has the current focus). The new image is an RGB image of exactly what is displayed on the screen, including things like ROI outlines.
- Utilities > Batch convert to NRRD: Allows the user to batch convert a set of .IM files into .NRRD files. Can also perform tracking of the image while converting.
- Utilities > Export… > Export All Derived (png): Exports all derived images (ratio, HSI and sum images) as .png files.
- Utilities > Close… > Close All Ratio Images: Closes all currently open ratio images.
- Utilities > Close… > Close All HSI Images: Closes all currently open HSI images.
- Utilities > Close… > Close All Sum Images: Closes all currently open sum images.
- Utilities > Generate Stack: Generates a new ratio or HSI image with independent scrollbars rather than the single plane ratio or HSI images that are generated by default.
- Utilities > Composite: Selecting this menu item will bring up a dialog which allows the user to quickly create a composite image with up to 4 channels. Any mass, sum, or ratio image can be used for the Red, Green, Blue, or Grey channels or a channel may be left blank. Each channel uses a simple color LUT. The min/max values for each LUT are taken from the underlying images. For example if the m26 mass image is used for the Red channel that channel will have the same min/max values. Changing the min/max values (or brightness/contrast) on the Contrast tab for the m26 image will automatically update the Red channel in the composite.
- Corrections > Apply dead time correction: Applies a dead time correction to the data. A 44 nanosecond correction is applied to the data.
- Corrections > Apply QSA correction: Applies a QSA correction to the data. Applying the QSA correction automatically applies a dead correction.
Developers
- Zeke Kaufman
- Joseph Collin Poczatek
- Boris Epstein
Contact Information
For inquiries regarding feature requests, bug report, or anything else related to the OpenMIMS plugin, please send email to:
nrims.software@rics.bwh.harvard.edu
License Information
Copyright 2010 NRIMS, National Resource for Imaging Mass Spectrometry. All rights reserved.
http://www.nrims.hms.harvard.edu/
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of this software and associated documentation files (the “Software”), copy, modify, merge, publish, or otherwise alter this software for educational or academic purposes subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
The copyright holders of other software modified and included in the Software retain their rights and the licenses on that software should not be removed.
Cite the NRIMS acknowledgement (above) in any publication that relies on the Software. Also cite those projects on which the Software relies when applicable. See the “About OpenMIMS” menu for the most up to date list.
If you would like to use or modify the Software for commercial purposes contact us.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED “AS IS”, WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.
OpenMIMS has modified, uses, or depends upon:
- TurboReg: http://bigwww.epfl.ch/thevenaz/turboreg/
- NRRD file format: http://teem.sourceforge.net/nrrd/
- nrrd plugins: http://flybrain.stanford.edu/nrrd
- jFreeChart: http://www.jfree.org/jfreechart/
- Apache Commons: http://commons.apache.org/io/
Please cite OpenMIMS or any of the above projects when applicable.